The mountain gorilla is one of subspecies of eastern gorilla. It is listed as endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, as its population consists of 1,004 individuals in two populations as of 2018. Some population lives in Biwindi Impenetrable National Park of Uganda, and other part of population live in the Virunga Mountains in three adjacent national parks, namely Uganda’s Mgahinga Gorilla Park, Rwanda’s Volcanoes National Park, and Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Here you are going to learn Why Are Mountain Gorillas Endangered and what is being done for Mountain Gorilla Conservation. So in order to raise awareness do not forget to share this page with your friends and family on your social media accounts.
Why Are Mountain Gorillas Endangered
- Mountain Gorillas are endangered due to the following reasons:
- Destructive human activities like deforestation
- civil wars
- poaching
- human interaction with Gorillas
- Forest clearance for human settlement is badly affecting the mountain Gorillas habitats.
- Presence of armed militia is putting mountain Gorillas lives in danger.
- Hunting of Gorillas is also a great threat to mountain Gorillas.
- Interaction of human with Gorillas causes spreading of diseases in Gorillas.
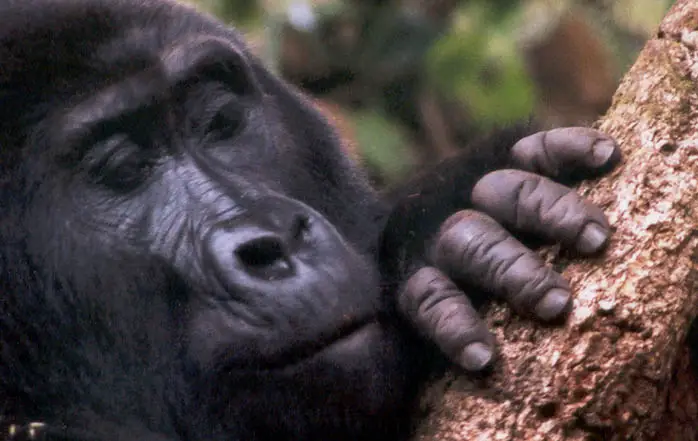

When Did Mountain Gorillas Become Endangered
- Mountain Gorilla is a subspecies of Eastern Gorilla. This subspecies was discovered in 1902.
- Since its discovery, it faces severe life threatening conditions like civil conflicts (wars), hunting, habitat destruction, poaching and diseases.
- These conditions were so severe that once it was thought that species might be extinct by the end of the 20th century.
- Due to conservation effort made in recent years, both the population of mountain gorillas have increased in numbers.
How Many Mountain Gorillas Are Left In The Wild
- Mountain gorillas survive in two regions only:
- Uganda’s Bwindi Impenetrable National Park
- Virunga Massif’s mountain- a chain of volcanoes spreading across Rwanda, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Once it was thought mountain gorillas will go extinct within the millennium but good news is that, according to recent census Gorillas numbers have increased as compared to previous census.
- According to the various census conducted the population of Mountain Gorillas have been as follows:
- in 1981 there were 254 Mountain Gorillas.
- in 1989 there were 329 Mountain Gorillas.
- in 2006 there were 302 Mountain Gorillas.
- in 2012 there were 400 Mountain Gorillas.
- in 2018 there were 1000 Mountain Gorillas.
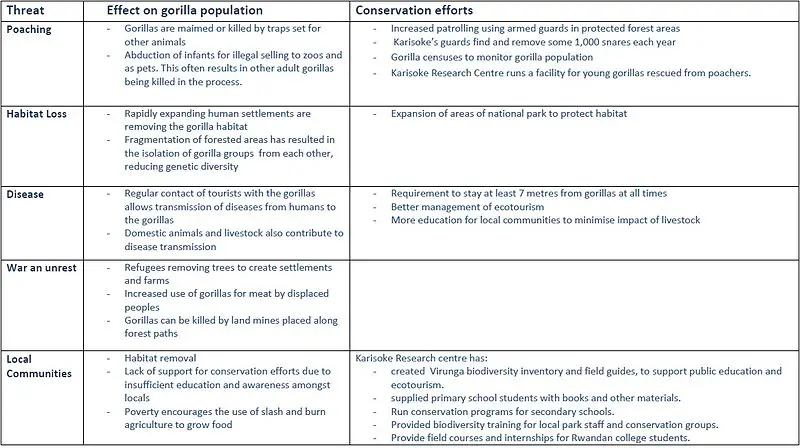
Mountain Gorilla Threats
Factors threatening the life of Mountain Gorillas:
- Poaching
- Habitat
- Diseases
- War and Civil Unrest
- Local Communities
1. Poaching
- Gorillas are caught in by the traps set for the other animals, causes the disability or death of Gorillas.
- Illegally catching and selling of infants to zoos and as pet, often results in killing of adult gorillas.
2. Habitat
- As human population is increasing rapidly and more area is required for their settlement. This causes the removal of Gorillas’ habitat.
- Forested area is fragmented which causes the isolation of Gorillas groups from each other, reducing genetic diversity.
3. Diseases
- Tourists regularly come in contact with Gorillas which might allow transmission of human diseases to Gorillas.
- Domestic and other animals, livestock are also one of the cause of transmitting of diseases to Gorillas.
4. War And Civil Unrest
- Gorillas are facing threats from fighting between rebel armies in and around the national parks.
- War refugees have increased the use of Gorillas meat as food.
- Land mines placed along forest path are also one of the cause of Gorillas’ killings.
5. Local Communities
- There is lack of education and awareness in local people about animal conservation.
- Poverty makes people to use slash and burn agriculture to grow food.
6. Mountain Gorilla Poaching
- The hunting, trading and consumption of Gorillas is almost universally illegal in all Congo Basin countries.
- However poaching continues as lack of enforcement of national and international laws and weak judiciary system.
- It’s not easy to estimate how many Gorillas are poached because they are hunted and eaten at the spot.
- Ratio of hunting gorillas is low as compared to other animals.
- Even low ratio of hunting of Gorillas makes its population decline because of its low reproductive rate.
What Are Mountain Gorillas Hunted For
Following are the reasons for hunting Gorillas
- Bush-meat
- Usage in Medicine
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Private Collection or Trophy
1. Bush meat
- Meat of many wild animals is eaten in West and central Africa which are not used in other parts of word.
- In remote areas of these regions, Gorillas are also hunted for their meat.
- Earning from selling gorillas meat is slightly higher than other meat, which increases average family income.
- Gorillas are injured or killed in traps or snares set for other animals.
2. Usage in medicine
- Mountain Gorillas are hunted, as its body parts are used in traditional medicines.
- The effectiveness of these medicines is not proven scientifically.
3. Illegal wildlife Trade
- All wildlife trade is not illegal but worrying is that a large proportion of it is illegal.
- Illegally catching and selling of infants to zoos and as pet, often results in killing of the parents gorillas.
4. Private collection or Trophy
- Gorillas are also victim of trophy hunting by wealthy people who takes pleasure in hunting them and make their bodies part of their collection.
- The storage of gorillas’ parts hve no scientific or educational use, they are irrationally put on display only.
Mountain Gorilla Poaching Facts
- Illegally hunt or catch on land that is not one’s own or in contravention of official protection is called Poaching.
- Gorillas are still endangered animal, and hunting is one of the key reasons.
- Gorillas’ meat is eaten in West and Central Africa.so they are hunted for meat as food.
- Hunting and poaching of gorillas is one of the income source for an average family as they sell their meat and body parts.
- Body parts are used by wealthy people for decoration as trophies which has no educational and scientific purposes.
- The body parts are also used in conventional medicines with no scientific proof for their effectiveness.
- Infants are illegally caught and sold to zoos and for keeping them as pet animals.
- At least 15 Virunga’s mountain Gorillas might have been killed during civil war in 1990.
- Between 1990 and 1992 4 Gorillas were killed, when a large number of Rwanda refugees took refuge in the camp at the edge of the Virunga National Park,
- A number of Gorillas killed is not know as they are killed and eaten up at the spot.
Mountain Gorilla Habitat Loss
- Gorilla habitat loss is one of the most severe threats to Gorilla population.
- The forests where Gorillas live are being rapidly cleared for human settlements causing loss of mountain Gorilla habitat.
- Fragmentation of forested area has resulted in the isolation of Gorilla groups from each other, reducing genetic diversity.
- Causes of deforestation or Gorilla habitat loss are:
- settlement of these areas for growing human population
- for agricultural purposes
- using wood for fire.
WWF Mountain Gorillas
- WWF is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961.
- WWF originally stood for “World Wildlife Fund” but name changed to “World Wide Fund” in 1986.
- WWF is working for wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment.
- WWF is working on mountain gorilla conservation as part of the International Gorilla Conservation Program (IGCP).
- IGCP was formed in 1991 as a coalition program which currently consists of WWF, Fauna and Flora international.
- It works in close partnership with the respective protected areas authorities of the three countries which are home to mountain gorillas: the Rwanda Development Board, the Uganda Wildlife Authority and the Institute Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature in DRC.
- In Virunga National Park, IGCP and WWF are working in collaboration with the Congolese Institute for Nature Conservation (ICCN), and supported:
- Environmental awareness and education
- Promotion of sustainable livelihoods
- Equipping and paying salaries for Virunga National Park staff
- In 2002, it provided additional funding to increase the number, duration, and coverage and anti-poaching patrols in Volcanoes National Park, leading to the arrest of poachers and a drastic reduction in poaching.
- Thanks to combined effort resulting in increase of Virunga population by 14%
- WWF is also active in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, the only other habitat of mountain gorillas.
Mountain Gorilla Conservation
- Mountain gorillas were declared as endangered animal in 1996 by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN).
- Now It’s the only great ape with increasing population.
- The number of gorillas were more than 1,000 individuals till 2018.
- WWF is working in close partnership with the respective protected areas authorities of the three countries which are home to mountain gorillas:
- the Rwanda Development Board
- the Uganda Wildlife Authority
- the Institute Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature in DRC.
Mountain Gorilla Conservation Status
- It is listed as endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, as its population consists of 1,004 individuals in two populations as of 2018.
- Mountain gorillas are not only threatened by their habitat loss by human encroachment, but also victim of human violence (civil war).
- Gorillas are also killed and caught by the poachers.
- Their body parts are also sold for using in medicine and also for decoration as trophy.
- Baby gorillas are also sold illegally to zoos and as pets.
What Is Being Done To Save The Mountain Gorilla – Saving Mountain Gorillas
The main International NGOs involved in conservation of mountain gorillas is the International Gorilla Conservation Program, which was established in 1991 as a joint effort of the African Wildlife Foundation, Fauna & Flora International and the World Wide Fund for Nature. Conservation requires work at many levels, from local to international, and involves protection. Dr. Dain Fossey broke down conservation efforts in three categories: Active, Theoretical and Community Based:
- Patrolling has been increased in protected forest area using armed guards to save gorillas from hunting and poaching.
- In September 1967, Dr. Dain Fossey established the Karisoke Research Center in Rwanda’s Virunga Mountains and set in motion one of the longest-running studies of any animal species anywhere in the world.
- Karisoke’s guards find and remove around 1000 traps and snares every year.
- Karisoke Research Center runs a facility for young gorillas rescued from poachers.
- Gorilla censuses are conducted to monitor gorilla population.
- The area of National Park has been expanded to protect gorilla habitat.
- To avoid diseases from human it is advised to stay at least 7 meter from gorilla all time.
- Better management of ecotourism.
- Karisoke Research Center has:
- Created Virunga biodiversity inventory and field guides, to support public education and ecotourism.
- Books and other material have been provided to the students of primary school.
- For secondary school students, conservation program are being run.
- Provided biodiversity training for local park staff and conservation groups.
- Rwanda college students are being provided with field courses and internships.
Mountain Gorilla Conservation Fund
- Mountain Gorilla Conservation Fund (MGCF) is dedicated to protection and conservation of endangered mountain gorillas in Africa and their habitat.
- MGCF is working with people around the National Parks.
- MGCF is doing this since 1983.
- It introduced veterinary medicine in 1986 through Mountain Gorilla Veterinary Project or Gorilla Doctors.
- In 1996 MGCF established a working relation with Makerere University in Kampala and started WARM Department (Wildlife Animal Resources Management) for teaching of wildlife medicine to the Africans make the project self sustainable.
- Today many students graduated from the university and working with wildlife in many national parks around Africa.
- These students also established an organization called Uganda Wildlife Veterinary Network.
- All these efforts making these animals a great comeback.
Why Are Mountain Gorillas Important – Mountain Gorilla Role In Ecosystem
- Naturally every living thing has a role to balance its environment or ecosystem.
- Gorillas also play an important role to balance their environment.
- As they consume large amount of vegetation, thus they maintain the balance in the food chain.
- Disruption of food chain could negatively affect other wildlife in the area.
- As more tourists visit to these areas to see gorillas, local business also grows.
- As business grows, earning of common people also increases.
- It is estimated that one mountain gorilla can indirectly generate £2.5 million over its lifetime from tourist income.
Leave a Reply